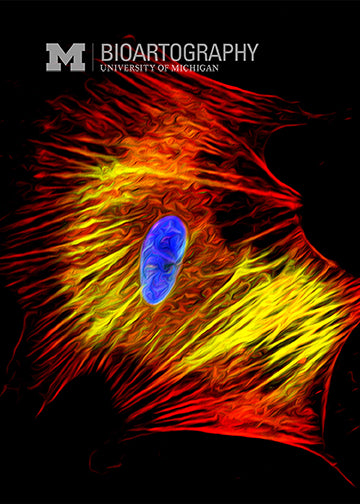
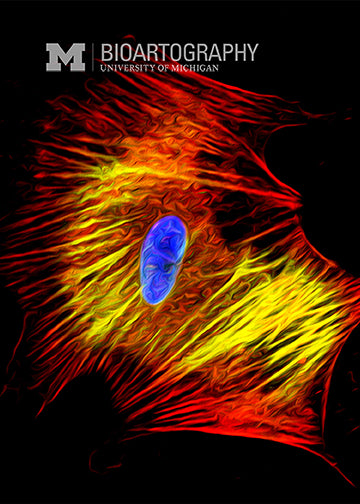
Yue Shao, Graduate Student Mechanical Engineering (Fu and Gumucio Laboratories), University of Michigan College of Engineering
Embryonic stem cells hold great promise for regenerative medicine because they have the potential to become any cell type in the body. Thus, they could be used to engineer tissues and organs to replace diseased or damaged ones, alleviating a need for organ and tissue transplants. The cell seen here is an engineered smooth muscle cell, generated in culture from human embryonic stem cells. Smooth muscle is a specialized form of muscle that is found in the GI tract and the urinary system. Very little is known about how smooth muscle develops in the embryo, so this culture system may reveal new discoveries about smooth muscle biology that could be used to diagnose or treat diseases of the muscle in those tissues.
16-034
