The Human Embryonic Stem Cell Center, University of Michigan
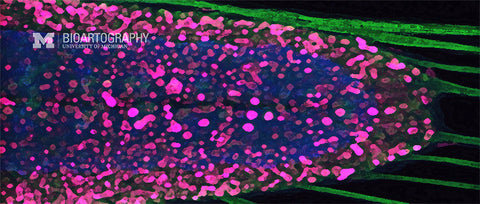
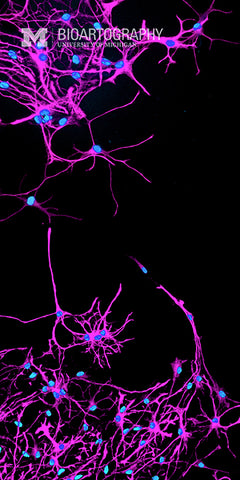
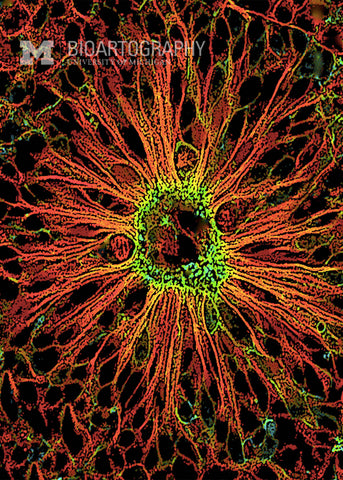
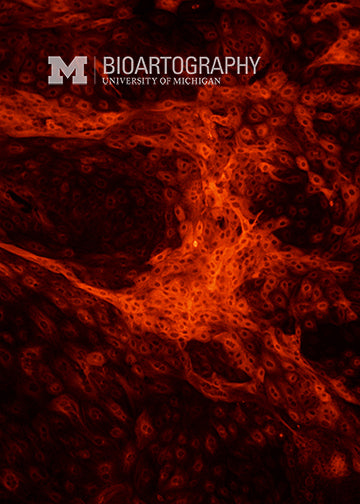
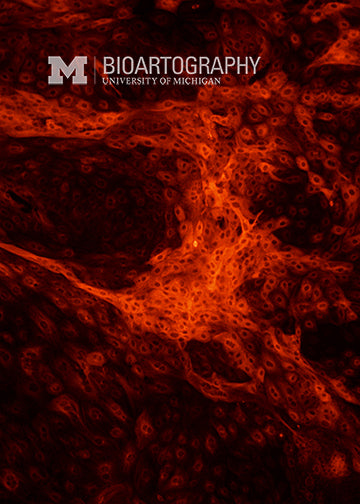
The goal of this work is to coax human embryonic stem (ES) cells to form neuronal cells of the brain and spinal cord. These ES cells were exposed to a growth factor called noggin that encourages them to differentiate into neuronal cells. The cells were then stained to determine if they express typical neuronal proteins (red). Using these cells, we can study the growth and development of primitive cells of the nervous system in a culture dish. Ultimately these studies should help us learn how to use similar cells to re-engineer damaged brains and spinal cords.