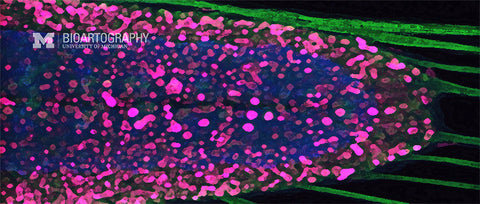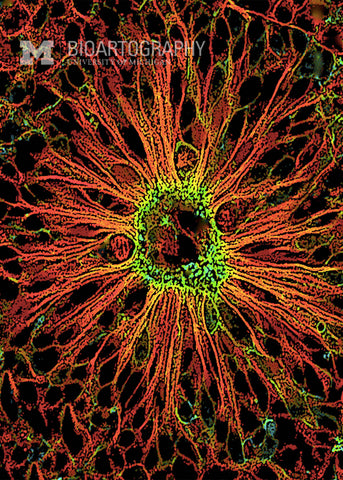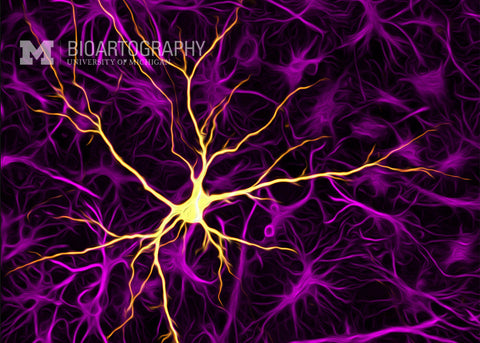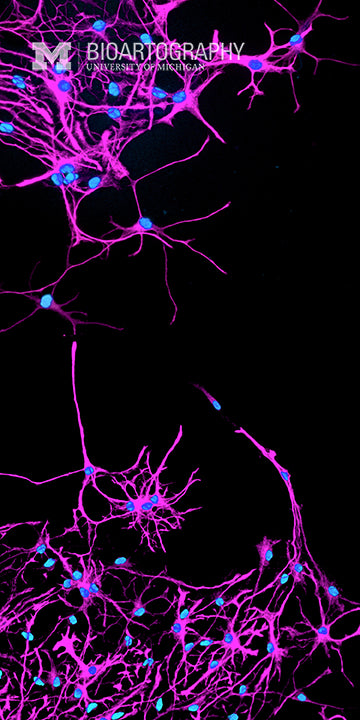
SunJung Kim, Ph.D., Postdoctoral Fellow, Center for Organogenesis and Internal Medicine, Division of Molecular Medicine and Genetics, University of Michigan Medical School
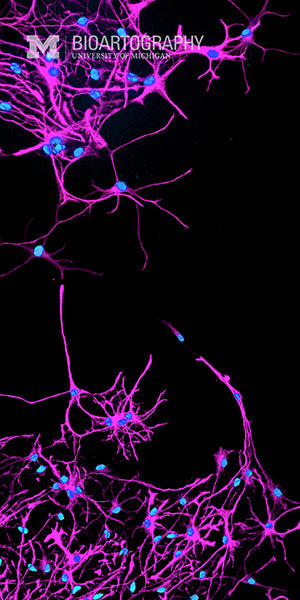
Astrocytes (astroglia) are star-shaped cells of the brain and spinal cord. They were originally thought to play mainly supportive roles, but recent data indicate that they are also important in repair of the brain and spinal cord following traumatic injury. These are cultured astrocytes that were differentiated from neural stem cells of the adult mouse brain. They are labeled here with an astrocyte specific marker (purple); cell nuclei are labeled with DAPI (blue). Astrocytes are thought to play a role in maintenance of the blood-brain barrier and their activity may control blood flow in the brain. New research suggests that these cells could be important in the development of depression in diabetics, as they are the only cells in the brain to carry insulin receptors.