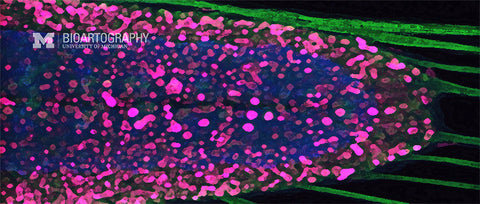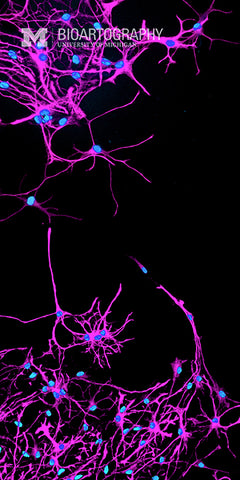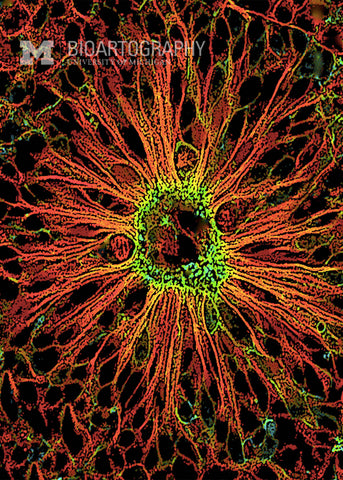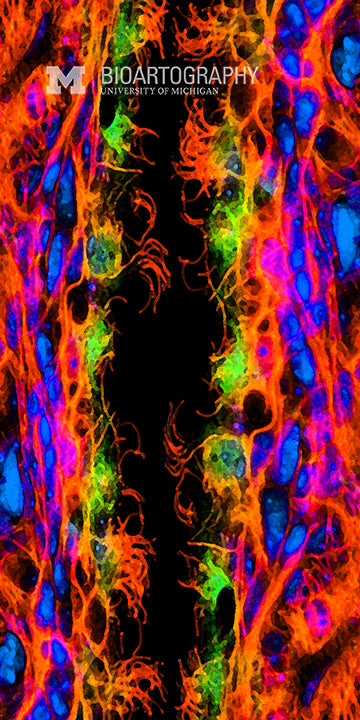
SunJung Kim, Ph.D., Postdoctoral Fellow, Center for Organogenesis and Internal Medicine, Division of Molecular Medicine and Genetics, University of Michigan Medical School
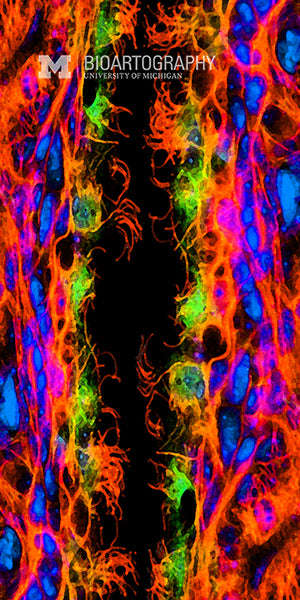
The brain contains a network of cavities called ventricles that are filled with cerebral spinal fluid (CSF). The ventricles are lined by cells called ependymal cells, here seen at the center, that contain hair-like projections called cilia (red). Ependymal cells act to promote the free exchange of nutrients between the CSF and the nervous tissue of brain and spinal cord. Recent studies suggest that under some conditions, ependymal cells might also act as stem cells to give rise to new neurons.