Aaron Udager, M.D./Ph.D., Graduate Student, Cell and Developmental Biology
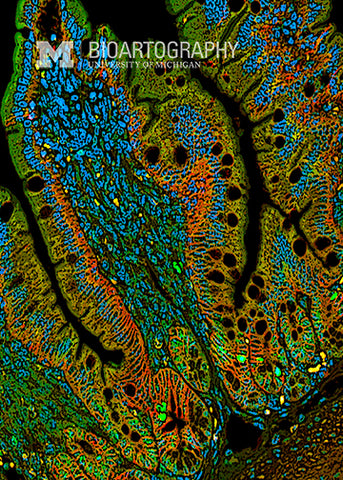
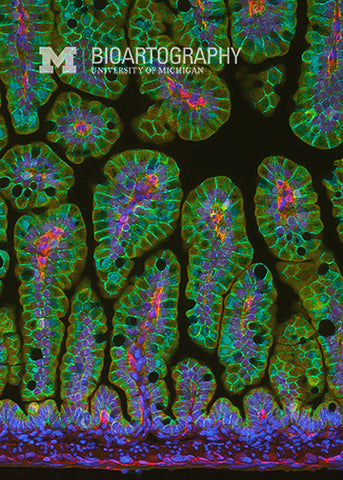
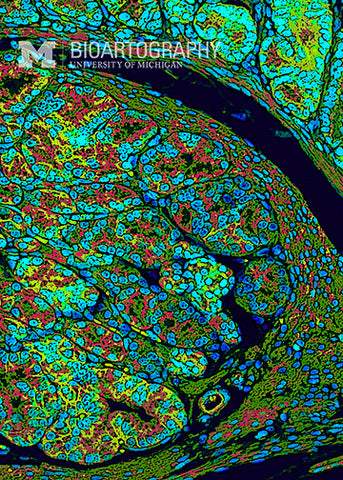
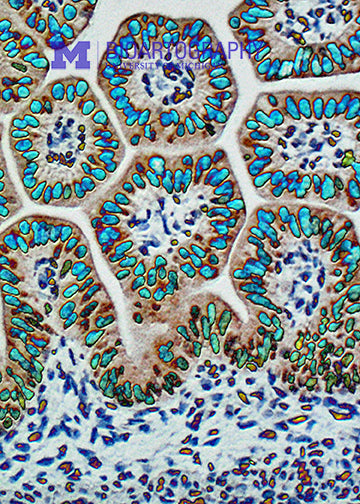
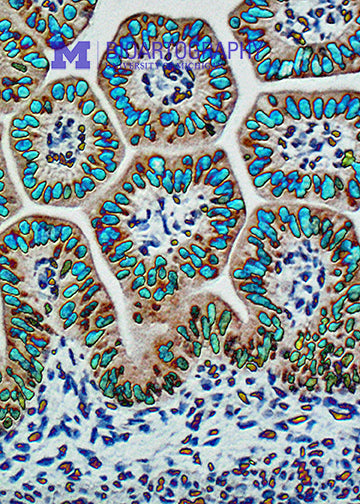
This is an image of a fetal mouse intestine. The brown cells with blue nuclei are intestinal epithelial cells. In the adult animal, these cells will be responsible for the processing and uptake of nutrients in the gut. Because the intestine needs a huge surface area for proper absorption, the epithelium is thrown into folds, called villi. Stem cells are located at the base of each villus and are responsible for replacing the entire epithelium every 3-4 days. The final surface area of the intestine in an adult human is approximately 2,000 square feet, bigger than many houses! Loss of villi occurs in Celiac disease, leading to malabsorption.
09-005